
Capuchin Monkey Habitat: Inside Their Remarkable World
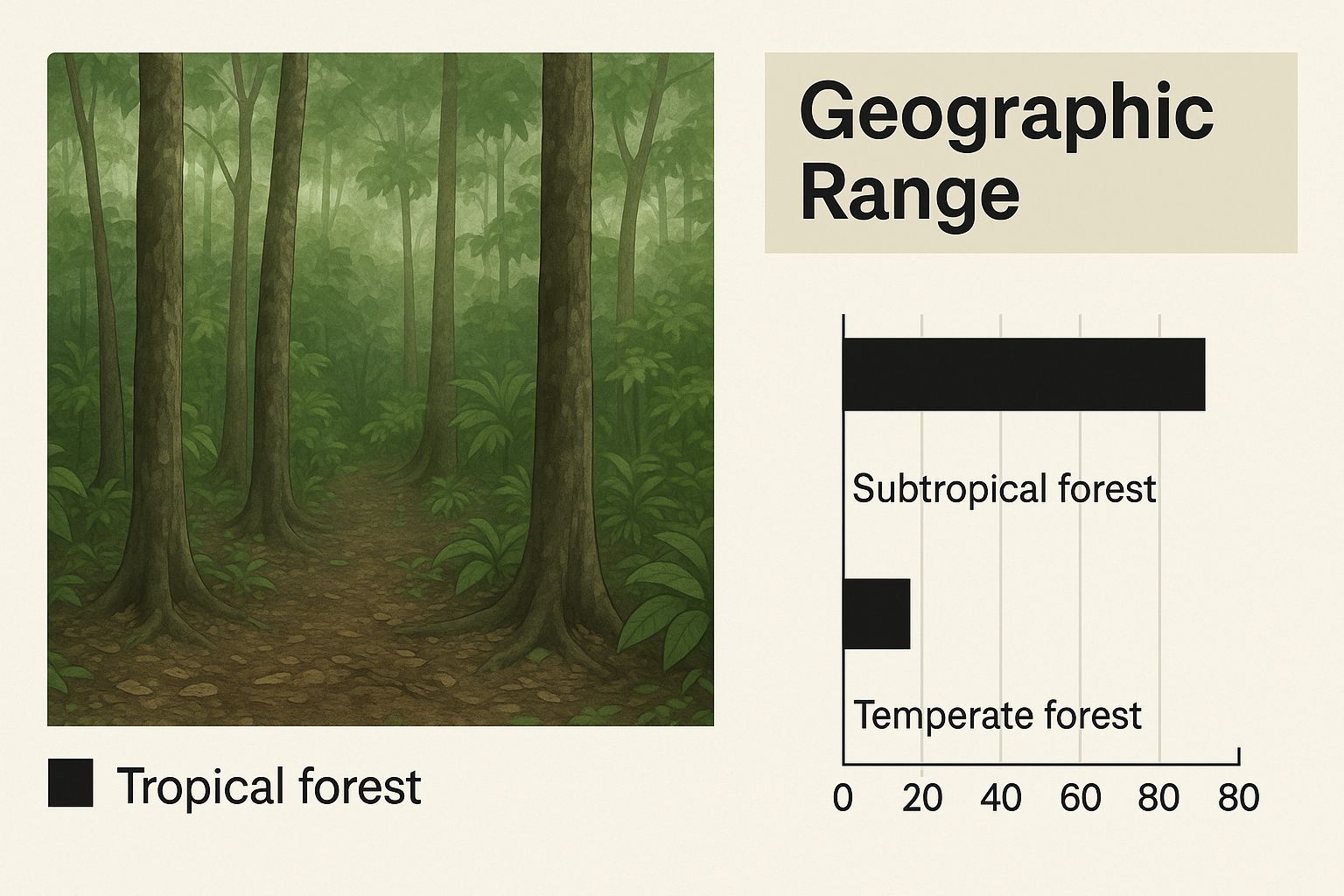
Mapping the Capuchin World: Their Geographic Range
Capuchin monkeys, renowned for their intelligence and adaptability, inhabit a remarkably diverse and expansive territory. Their range stretches across a significant swathe of Central and South America, a testament to their ability to flourish in various environments. This wide distribution reflects their evolutionary success and underscores the crucial role habitat plays in their survival. Understanding this range is essential for conservation initiatives, as it helps pinpoint key areas for protection and exposes potential vulnerabilities to environmental shifts.
From Central America To The Southern Cone: A Continent-Spanning Presence
The capuchin monkey’s habitat encompasses an impressive array of landscapes, from the vibrant rainforests of Central America to the more arid forests of South America. However, their distribution isn't uniform. Different capuchin species have carved out distinct niches within this vast area. For instance, the white-faced capuchin is common in Central America, inhabiting countries like Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Their range continues along the coast of Colombia and Ecuador, showcasing their impressive adaptability. Astonishingly, some individuals have even been observed as far south as Argentina. Capuchin monkeys are widely distributed across Central and South America, boasting one of the largest ranges among New World monkeys. Learn more about capuchin distribution. This adaptability speaks to their resilience when faced with environmental changes and human activity.
Environmental Influences: Shaping The Capuchin Distribution
Several factors influence where capuchin monkeys live within their range. Resource availability, encompassing food and water sources, plays a significant role. Regions with abundant fruit, insects, and other food sources are more likely to support larger capuchin populations.
Furthermore, the presence of predators can shape their distribution. Capuchins tend to avoid areas with high predator densities, seeking safer havens in habitats offering better protection. Competition with other primate species also influences where different capuchin species establish their territories. This complex interplay of environmental factors creates a dynamic tapestry of capuchin populations across their range.
Human Impact and Conservation Concerns: Protecting Capuchin Habitats
While capuchins have demonstrated remarkable resilience, human actions pose significant threats to their homes. Deforestation, driven by agriculture and logging, leads to habitat loss and fragmentation. This fragmentation isolates capuchin populations, diminishing genetic diversity and escalating their susceptibility to disease and other dangers.
Historically, their range has fluctuated due to environmental changes and human impacts, including deforestation and habitat fragmentation. These activities reduce both habitat quality and availability, presenting significant threats to capuchin populations. This underscores the urgent need for conservation efforts focused on protecting and restoring capuchin habitats.
Creating corridors between fragmented forests and promoting sustainable land management practices are crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of these intelligent and adaptable primates. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing human needs with the preservation of these vital ecosystems.
Forest Diversity: Where Capuchins Call Home
Capuchin monkeys display an incredible adaptability, thriving in a surprisingly diverse range of forest ecosystems across Central and South America. This ability to navigate and flourish in various forest types is a key factor in their wide distribution. From the dense, tangled canopies of tropical rainforests to the more open, seasonally dry forests, these clever primates have developed specialized survival strategies for each unique environment. These diverse habitats influence every aspect of their daily lives, shaping their foraging techniques, social interactions, and even their predator avoidance methods.
Rainforest Residents: A Three-Dimensional World
In the vibrant, multi-layered world of the tropical rainforest, capuchin monkeys showcase remarkable agility. The intricate structure of these forests provides abundant opportunities for foraging, socializing, and finding safe haven. They expertly utilize the different canopy layers throughout the day. For instance, they might spend their mornings foraging for fruits and insects in the lower canopy, later ascending to the higher canopy for afternoon rest and social grooming. This vertical stratification of their habitat allows them access to a diverse array of resources while minimizing competition.
This visualization offers a ground-level perspective of a dense tropical rainforest within the capuchin monkey's range, highlighting the complex terrain they navigate. The thick undergrowth and diverse tree trunks emphasize the challenging yet resource-rich environment these primates call home, making their adaptability all the more impressive.
Adapting to Dry Forests: Resourcefulness in a Changing Landscape
Unlike the consistent humidity of rainforests, dry forests present a unique set of challenges. These forests experience distinct wet and dry seasons, resulting in fluctuating food availability. During the dry season, capuchins demonstrate remarkable resourcefulness, incorporating less desirable foods into their diet and increasing foraging efforts. They may also travel longer distances to find water, showcasing their flexibility in the face of environmental change. You can explore more about regional variations in capuchin monkey habitats.
To better understand the diverse habitats capuchin monkeys occupy, let's take a closer look at the following table:
This table provides a comparison of the different forest ecosystems where capuchin monkeys can be found, including key characteristics and how capuchins utilize each habitat type.
| Habitat Type | Elevation Range | Key Characteristics | Capuchin Adaptations | Main Food Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tropical Rainforest | Lowland to 1000m | High humidity, dense canopy, abundant biodiversity | Agile movement through canopy layers, diverse diet | Fruits, insects, small vertebrates, leaves |
| Dry Deciduous Forest | Lowland to 1500m | Distinct wet and dry seasons, open canopy, fewer resources | Increased foraging effort during dry season, adaptable diet | Fruits, seeds, flowers, insects, tree gum |
| Montane Forest | 1000m to 2000m | Cooler temperatures, cloud cover, unique flora and fauna | Thicker fur for insulation, specialized foraging techniques | Fruits, insects, mosses, lichens |
| Mangrove Forest | Coastal areas | Brackish water, tangled roots, specialized vegetation | Ability to swim, foraging in intertidal zones | Crabs, mollusks, insects, fruit |
As this table demonstrates, capuchins exhibit a range of adaptations to thrive in these varied environments.
The Importance of Forest Structure: Shelter and Sustenance
Whether in a rainforest or a dry forest, the forest's structure plays a crucial role in capuchin monkey survival. The availability of dense foliage provides protection from predators like eagles and jaguars. The interconnected branches of the canopy offer efficient travel routes, allowing them to quickly move through their territory. The diversity of tree species ensures a varied diet, with access to fruits, leaves, insects, and other food sources.
Capuchin monkeys inhabit a diverse range of habitats, from lowland tropical rainforests and mountain forests up to 2,000 meters to dry deciduous forests, mangrove swamps, secondary forests, and even disturbed areas. Learn more about these fascinating creatures at SeeTheWild. This adaptability is vital for maintaining viable populations. Their range stretches from Honduras to Brazil and Paraguay, covering both lowlands and elevated regions. However, habitat fragmentation poses a growing threat by reducing suitable habitat and increasing competition. While they can adapt to high elevations, their populations in these areas are often fragmented, raising concerns about long-term viability.
Habitat Loss and Conservation: Protecting Crucial Ecosystems
The survival of capuchin monkeys depends heavily on the preservation of their forest homes. Deforestation and habitat degradation are shrinking their natural range at an alarming rate. Habitat loss not only restricts access to vital resources but also forces them into closer contact with humans, escalating the risk of conflict and disease transmission. Protecting these vital ecosystems is crucial for maintaining healthy capuchin populations and ensuring the biodiversity of these vital South and Central American forests.
Territory Masters: How Capuchins Manage Their Domain
Capuchin monkeys, known for their playful antics, possess a surprisingly serious side when it comes to their territory. These clever primates demonstrate a deep understanding of their surroundings, moving through and managing their domain with remarkable skill. Their spatial intelligence allows them to map out essential resources, establish boundaries, and adjust to environmental shifts within their home range. This intricate knowledge of their world plays a vital role in their survival and social interactions.
Defining the Capuchin Domain: Home Range and Territory
Understanding a capuchin's territory requires looking at two key concepts: home range and territory. The home range is the overall area a group regularly uses for daily activities like foraging, sleeping, and socializing. Within this larger home range is the territory, the specific area they actively defend from other capuchin groups. The size of a home range can fluctuate quite a bit based on a variety of factors.
The home range size varies considerably based on the capuchin species and their specific habitat. The tufted capuchin, for example, has an average home range of 8-9 km² (3.1-3.5 mi²). This expansive area allows them to access a diverse range of habitats, including rainforests and various edge habitats, typically sticking to the understory and lower to middle canopy. Factors such as the availability of food, competition, and predation risk all influence the size of the home range. Discover more insights about the tufted capuchin. For example, an area rich in resources might result in a smaller home range, while scarce resources necessitate a larger one.
Factors Influencing Territory Size: A Balancing Act
A capuchin group's territory isn't fixed; it's constantly changing based on the environment and the group's needs. Resource availability is a major factor. In areas with plentiful food and water, territories can be smaller because resources are easy to come by. Conversely, in areas with limited resources, territories tend to be larger to ensure the group has enough.
Group size also matters. Larger groups generally need larger territories to support their greater needs. This becomes especially important when resources are scarce, as competition within the group can increase. Competition with other capuchin groups, or even other primate species, can also affect territory size. Highly desirable areas with valuable resources can lead to smaller, fiercely protected territories.
Navigating the Domain: Spatial Memory and Efficient Travel
Capuchins exhibit impressive spatial memory, enabling them to efficiently travel within their home range and locate essential resources. They build mental maps of their territory, remembering the locations of fruit trees, water sources, and safe places to sleep. This internal map helps them optimize their daily routes, getting the most out of foraging trips while conserving energy, much like a savvy shopper navigating a familiar grocery store.
Furthermore, capuchins display signs of planning their foraging expeditions. They visit various resource patches based on their ripening cycles, demonstrating a complex awareness of their environment and its changes over time. They adapt their strategies based on the season, concentrating on specific resources when they are most abundant.
Territorial Defense: Maintaining Control and Access to Resources
Although generally social creatures, capuchins fiercely defend their territory. Intergroup encounters at territorial boundaries often involve vocalizations, aggressive displays, and even physical confrontations. These encounters serve to reinforce boundaries and maintain access to crucial resources. Dominant males typically take the lead in defending the territory, heading the defense against intruders.
The social dynamics within the group also influence territoriality. A well-organized group with strong leadership is better equipped to defend its territory against rivals. This underscores the importance of social bonds not just for group stability, but also for securing vital resources. Capuchins have developed a complex system of territorial management, adapting their strategies to the challenges and opportunities presented by their environment.

Life in the Canopy: Vertical Habitat Strategies
Capuchin monkeys are truly masters of their arboreal domain. Their world isn't just the forest floor, it's a vibrant, three-dimensional tapestry woven from the ground to the highest branches. Understanding how these clever primates navigate and exploit this vertical landscape is key to appreciating their remarkable adaptability.
A Vertical Mosaic: Utilizing Different Canopy Layers
Imagine the forest canopy as a multi-layered buffet. Capuchins don't just dine randomly; they strategically select different levels for specific activities. The lower canopy, teeming with fruits and insects, is their primary foraging ground. But when it comes to rest or escaping predators like jaguars, they ascend to the safer heights of the upper canopy. This strategic use of vertical space optimizes their access to food while minimizing their vulnerability.
They switch between these levels throughout the day, much like we might move between different rooms in our homes. The forest, for them, is a dynamic living space, and their movements reflect the ever-changing demands of their daily routines.
The Prehensile Tail: A Key to Canopy Mastery
Crucial to their arboreal acrobatics is their prehensile tail, a remarkable adaptation that serves as a fifth limb. This extra "hand" provides incredible stability and mobility as they navigate the intricate network of branches. Picture it as a built-in safety line, enabling them to reach for otherwise inaccessible fruits or swing effortlessly between trees. This unique appendage is a game-changer in their vertical world.
Forest Structure and Movement: Navigating a Complex Maze
The architecture of the forest itself plays a significant role in how capuchins move and utilize their vertical habitat. In dense, interconnected rainforests, they can travel extensively through the trees, establishing what might be considered travel highways high in the canopy. This allows them to efficiently navigate their territory without ever having to descend to the more dangerous forest floor. In more fragmented forests, however, they're often forced to travel on the ground, increasing their risk of encountering predators.
Seasonal Shifts and Vertical Strategies
Resource availability also impacts vertical habitat use. During the dry season, when food becomes scarcer in the lower canopy, capuchins demonstrate remarkable flexibility. They may venture down to the forest floor or up into the higher canopy in search of alternative food sources. This seasonal shift highlights their adaptability and resourcefulness in coping with environmental change.
To better understand how capuchins use the different layers of the forest, let's take a look at the following data table:
Vertical Habitat Usage by Capuchin Monkeys
This table presents data on how capuchin monkeys utilize different vertical layers of the forest canopy for various activities throughout their daily routines.
| Canopy Layer | Height Range | Primary Activities | Time Spent (%) | Key Adaptations Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest Floor | Ground level | Foraging for fallen fruit, insects, and small vertebrates | 10-15% | Terrestrial locomotion, keen sense of smell |
| Lower Canopy | 5-15m | Foraging for fruits, insects, and leaves; social interactions | 40-50% | Agile climbing, prehensile tail for stability |
| Middle Canopy | 15-25m | Resting, social grooming, predator avoidance | 20-25% | Prehensile tail for support, keen eyesight |
| Upper Canopy | 25m+ | Traveling between trees, escaping predators | 10-15% | Prehensile tail for balance, powerful leaps |
As shown in the table, capuchins spend a significant portion of their time in the lower canopy, where food is most abundant. However, they also make use of all other layers, demonstrating their remarkable adaptability. It's important to note that these percentages can vary depending on factors like the specific species, location, and season.
Understanding the intricate relationship between capuchins and their vertical habitat is critical for conservation. Protecting the diverse structure of forests, particularly the integrity of the canopy, is essential for ensuring these highly intelligent primates continue to flourish in their complex arboreal world.
Seasonal Survivors: Adapting to Nature's Rhythms
Capuchin monkeys thrive in diverse forest ecosystems, demonstrating a remarkable ability to adapt to the ever-changing seasons. Their survival depends on a deep understanding of the rhythmic shifts in their environment. This allows them to adjust their behaviors, diet, and movements in response to nature's fluctuations. This intricate dance with the seasons showcases their intelligence and resilience.
Following the Fruitful Cycle: A Seasonal Feast
One of the most fascinating aspects of capuchin adaptability is their dietary flexibility. These primates possess an amazing ability to track the ripening of fruits throughout their territory. They develop a cognitive map of their surroundings, knowing exactly when and where specific fruits will be in season. This knowledge is crucial, especially during times of scarcity.
During the dry season, when fruit is less available, capuchins turn to alternative food sources. They display impressive resourcefulness, incorporating less desirable foods like insects and leaves into their diet. This flexibility ensures their survival through lean periods.
Ingenious Insect Hunters: Adapting Foraging Techniques
Capuchins are not solely fruit-eaters; they are opportunistic omnivores. This means their diet includes a wide variety of foods, including insects. They've developed specialized techniques for extracting insects from tree bark, leaf litter, and other hiding places. These skills become particularly valuable during specific seasons when insect populations flourish.
Their foraging techniques are not fixed; they change with the seasons. For example, they may employ different extraction methods depending on the kind of insect prevalent at a particular time of year. This adaptable foraging behavior highlights their resourcefulness and ingenuity.
Social Dynamics and Seasonal Shifts: Weathering the Lean Times
Seasonal changes influence not only food availability but also the dynamics within capuchin groups. During periods of abundance, groups might be larger and more spread out. However, when resources become scarce, particularly during the dry season, groups often become smaller and more tightly knit. This shift in social structure can help reduce competition for limited food.
These social adaptations emphasize the importance of cooperation within capuchin groups. In times of hardship, working together and sharing resources can be essential for survival. This social resilience underscores the effectiveness of their complex social structures.
Passing Down Ecological Wisdom: Intergenerational Knowledge Transfer
Knowledge of seasonal rhythms is not instinctive; it is learned. Younger capuchins learn from their elders, observing their foraging techniques and memorizing the locations of vital resources. This intergenerational knowledge transfer is essential for their continued survival.
This learning process is like a cultural inheritance, passing crucial ecological information down through the generations. This cultural adaptation, along with their natural intelligence, enables them to flourish in a constantly changing environment.
Climate Change Disrupting Rhythms: A Threat to Capuchin Survival
The carefully honed seasonal adaptations of capuchins face a growing threat from climate change. Changes in temperature and rainfall patterns are disrupting the timing of fruit ripening and insect emergence. These shifts can cause mismatches between capuchin behavior and resource availability, leading to potential food shortages.
Furthermore, more frequent and intense droughts can worsen resource scarcity, putting additional strain on capuchin populations. The increasing unpredictability of weather makes it more challenging for them to rely on their traditional ecological knowledge. Understanding these impacts is critical for creating effective conservation strategies to protect these adaptable and intelligent primates. Learn more about adopting a spider monkey for further primate information.
Under Threat: Challenges to Capuchin Monkey Habitats
Capuchin monkey habitats are facing mounting pressure. These threats jeopardize the survival of these clever primates. Understanding these threats is the first step towards protecting them. This means looking at both the obvious and the more subtle dangers impacting these crucial ecosystems.
Deforestation and Agricultural Expansion: Shrinking Forest Homes
One of the biggest threats to capuchin monkey habitats is deforestation. Driven by the ever-expanding need for agricultural land and logging, enormous areas of forest are being cleared. This leaves capuchins with less space to live and fewer resources. This habitat loss pushes them into smaller, isolated forest fragments, increasing their vulnerability to predators and disease.
This loss goes beyond just trees. It's the destruction of a complex ecosystem that supports a wide variety of life. Removing trees upsets the delicate balance of the forest, affecting everything from food and water availability to the complex relationships between species.
Forest Fragmentation and Isolation: Breaking Connections
Forest fragmentation creates isolated "islands" of habitat. This isolation has serious repercussions for capuchin populations. Smaller, isolated groups have reduced genetic diversity, making them more susceptible to disease and less adaptable to environmental change. Fragmentation also restricts their movement between areas, hindering their search for food and mates.
Imagine each isolated forest patch is a life raft. Some rafts will inevitably have fewer resources or be more vulnerable to capsizing. If the monkeys can’t move between rafts, their overall survival rate drops.
Edge Effects: Altering Microclimates and Food Webs
The creation of forest edges, where forests meet cleared land, introduces edge effects. These effects change the forest's microclimate, making it hotter, drier, and windier. These altered conditions negatively affect the plants and animals capuchins depend on.
Edge effects also disrupt the forest's intricate food web. For example, certain plants that thrive in the changed conditions of forest edges may overtake the native plants capuchins prefer, impacting insect populations and other animals that rely on those native plants.
Increased Predation and Human-Wildlife Conflict
As capuchin habitats shrink and become fragmented, these monkeys are forced into closer contact with humans and domestic animals. This increases predation from dogs and exposes capuchins to new diseases.
It also elevates the risk of human-wildlife conflict. Capuchins might raid crops for food, leading to retaliatory killings by farmers. This creates tension between human communities and these primates, making conservation efforts more challenging.
Conservation Success Stories: Protecting Capuchin Habitats
Despite these challenges, there are conservation successes. Creating protected areas and wildlife corridors that link fragmented forests can greatly improve capuchin survival rates. Sustainable forestry practices that minimize habitat disturbance also help preserve these vital ecosystems. As habitats face growing threats, even considering eco-friendly takeout containers contributes to conservation efforts.
These initiatives show that it is possible to meet human needs while also protecting capuchin monkeys and other forest inhabitants.
The Future of Capuchin Habitats: A Call to Action
The future of capuchin monkeys rests on the decisions we make now. Protecting their remaining habitat, lessening the impacts of deforestation and fragmentation, and encouraging sustainable land management are critical.
The loss of capuchin monkey habitat means more than the decline of a single species. It represents the unraveling of a vital and complex ecosystem. Protecting these habitats is essential not only for the survival of capuchins, but for the biodiversity and ecological health of our planet.
Conservation Lessons From Nature's Adaptability Masters
Capuchin monkeys are truly remarkable creatures, flourishing in a wide array of habitats across Central and South America. Their adaptability is a testament to their intelligence, flexible diet, and complex social structures. These characteristics allow them to navigate and even thrive in environments impacted by human activities. But how far does this adaptability truly stretch? Understanding both its strengths and limitations is essential for successful conservation efforts.
The Power of Flexibility: Thriving in a Changing World
Capuchins are resourceful problem-solvers. Their intelligence allows them to exploit new food sources and adjust their foraging behavior in the face of environmental change. For example, they’ve been seen using tools to access difficult-to-reach insects or crack open tough nuts, demonstrating an impressive capacity for innovation. Their omnivorous diet also provides a significant advantage. Unlike primates with specialized feeding habits, capuchins can switch between fruits, insects, leaves, and even small vertebrates depending on availability. This dietary flexibility helps them endure periods of food scarcity that might severely impact other species.
Their complex social structures also play a crucial role. Group living provides benefits like improved foraging efficiency and better predator detection. For instance, some capuchin groups have developed mutually beneficial relationships with squirrel monkeys, relying on the smaller primates to warn them of ground predators while they scan for aerial threats. These cooperative strategies enhance their survival in challenging and changing environments.
Limits to Adaptability: When Flexibility Isn't Enough
While capuchins are highly adaptable, their resilience isn't infinite. Habitat loss and fragmentation present serious threats. As forests shrink and become isolated, capuchin populations become increasingly vulnerable. This isolation restricts their access to essential resources and elevates the risk of inbreeding, decreasing genetic diversity and making them more susceptible to diseases. Even the most adaptable species have ecological breaking points when habitat degradation reaches a certain threshold.
Climate change and its disruption of seasonal patterns present a growing concern. Capuchins have evolved finely tuned adaptations to seasonal changes in their environment. However, changing temperatures and rainfall patterns can disrupt these rhythms, impacting the availability of food resources. For example, shifting fruit ripening cycles can lead to food shortages during critical periods, impacting the delicate balance they’ve established with their environment.
Conservation Strategies: Balancing Adaptability and Habitat Protection
Effective capuchin conservation demands a nuanced approach. Simply relying on their flexibility to cope with ongoing environmental pressures is insufficient. We must actively protect and preserve the habitats these remarkable primates rely on. You can contribute by supporting conservation efforts, which can be as simple as choosing eco-friendly options in your daily life, like using eco-friendly takeout containers. Learning more about primates can also help, such as exploring the possibility of adopting a spider monkey.
Protecting Crucial Habitats: Key Conservation Initiatives
Habitat connectivity is crucial. Establishing wildlife corridors that connect fragmented forest patches allows capuchins to move more freely, promoting gene flow and access to resources. Sustainable forest management practices that minimize habitat disruption are also vital. This involves careful logging practices and reforestation efforts that maintain the forest’s complexity, providing essential canopy cover and a diverse range of food sources.
Finally, community-based conservation projects that involve local communities in habitat protection are paramount. These programs empower local people to become stewards of their environment, ensuring that conservation efforts are aligned with local needs.
By integrating an understanding of capuchin adaptability with targeted habitat protection, we can secure a more resilient future for these primates and the communities that share their world.
Are you captivated by primates and considering adding one to your family? PrimatePet offers a selection of exotic companions, including marmosets, macaques, capuchins, and squirrel monkeys. We provide expert guidance on responsible pet ownership, from habitat setup and training to legal requirements and long-term care. Visit PrimatePet today to explore our available pets and discover how to provide a loving and enriching home.
Article created using Outrank




