
Exotic Pet Laws by State: Know the Key Regulations
Navigating the Wild West of Exotic Pet Ownership
Thinking of owning an exotic pet? Exotic pet laws by state vary significantly. This listicle covers the specific regulations in seven states, including Florida, Nevada, California, Texas, Ohio, Arizona, and New York. Understanding these exotic pet laws by state is crucial for responsible ownership and avoiding legal issues. Whether you’re interested in primates, birds, or reptiles, this guide provides essential information for first-time owners, experienced enthusiasts, and veterinary professionals alike. Learn the rules and make informed decisions about exotic pet ownership.
1. Florida Exotic Pet Regulations
Florida stands out when discussing exotic pet laws by state, boasting one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks in the United States. This system aims to balance the desire for exotic pet ownership with public safety and animal welfare. Florida categorizes animals into a three-tiered system based on their potential danger, creating a clear structure for prospective owners to navigate. This structured approach is why Florida earns its place at the top of this list.
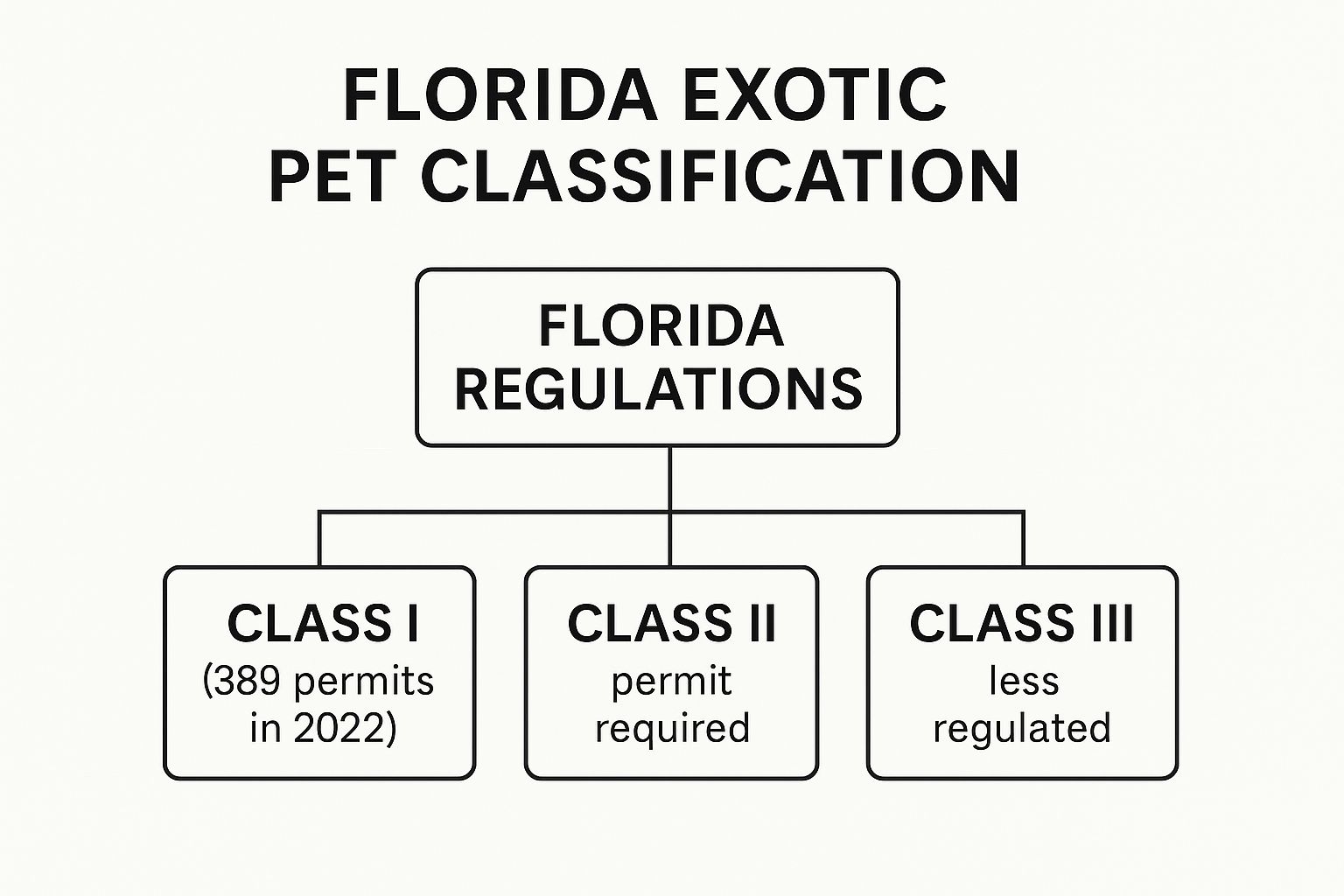
The infographic above visualizes the hierarchical structure of Florida's exotic pet permitting system. It highlights the three classes of animals and the escalating permit requirements and associated costs as you move from Class III to Class I. This tiered system allows ownership of a wide range of species while ensuring appropriate safeguards are in place for the more dangerous animals.
The state's three-tiered classification system designates animals as Class I (dangerous), Class II (concern), and Class III (less regulated). Class I animals, such as primates, big cats, and bears, pose the greatest potential danger to people. Class II animals, including many reptiles and some mammals, present a moderate risk. Class III animals are generally considered lower risk. Permitting requirements, housing standards, and oversight increase with the animal's classification level. For example, Class I and II animals require permits, while Class III animals generally do not. Specific cage sizes, security measures, and even prior experience handling the specific animal are mandated. Annual inspections are required for Class I and II permit holders to ensure compliance.
This tiered system helps prospective owners understand the responsibilities associated with different species. Detailed permit applications, including proof of experience and liability insurance, are required for Class I and II animals. The permitting process ensures owners are prepared for the challenges of exotic pet ownership.
Pros:
- Allows ownership of a diverse range of exotic species with the appropriate permits.
- The clear regulatory framework provides guidance for prospective owners.
- The inspection system contributes to animal welfare and public safety.
Cons:
- High permit fees (starting at $100 and exceeding $250 annually for Class I animals).
- Strict liability insurance requirements ($10,000 for Class I animals).
- Detailed record-keeping adds an administrative burden.
- Some municipalities have stricter regulations than the state, adding complexity.
Florida's regulations have seen documented success. As of 2022, the state had issued 389 Class I animal permits, indicating a significant number of individuals are engaging with the system. The state’s exotic pet amnesty program demonstrates a commitment to responsible pet ownership, having rehomed over 6,000 surrendered exotic pets since 2006.
Tips for navigating Florida's exotic pet regulations:
- Contact the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) before acquiring any exotic animal. They are the ultimate authority and can provide specific guidance based on the species you are considering.
- Consider joining the Florida Association of Reptile Keepers for support and resources in navigating the regulatory landscape. This community can offer valuable insights and practical advice.
- If you need to surrender an exotic pet, attend a Florida exotic pet amnesty day. This program provides a safe and responsible way to rehome animals without penalty.
Florida's regulations have been popularized not only by the FWC but also by figures like Doc Antle of Myrtle Beach Safari (featured in the Netflix series "Tiger King"), who operates under Florida's regulatory system. While his practices have been subject to scrutiny, his presence highlights the complexity and reach of Florida's exotic animal laws.
When considering acquiring an exotic pet in Florida, research and preparation are key. Understanding the state's regulations is crucial for both the well-being of the animal and your compliance with the law.
2. Nevada's Permissive Exotic Animal Laws
Nevada stands out when examining exotic pet laws by state, boasting one of the most lenient regulatory frameworks in the United States. This permissive approach allows private citizens to own a wide variety of exotic animals that are strictly prohibited in many other states. While this offers exciting possibilities for exotic animal enthusiasts, it's crucial to understand that this freedom comes with its own set of complexities, particularly concerning varying local ordinances. Nevada’s approach prioritizes individual ownership rights, placing less emphasis on state-level oversight compared to stricter states.

This system works by establishing minimal state-level restrictions while empowering individual counties and municipalities to enact their own, often more stringent, regulations. This means that while owning a big cat might be permissible under state law, your specific city or county might have ordinances forbidding it. This decentralized approach creates a complex legal landscape, highlighting the need for thorough research before acquiring any exotic animal in Nevada. For example, while the state doesn't mandate permits for most exotic pets, importing animals requires health certificates, showcasing a focus on disease control rather than ownership restriction. No state inspections are required for private owners, further emphasizing the limited oversight at the state level.
Nevada's unique approach to exotic pet laws by state has resulted in some notable examples. Several large private exotic animal collections exist, predominantly in the state’s more rural counties. Perhaps the most well-known example is the late entertainers Siegfried and Roy, whose famed Las Vegas tiger act thrived under Nevada law until the tragic 2003 incident. Their case underscores both the potential and the inherent risks associated with private ownership of large predators.
Pros:
- Greater Freedom for Exotic Animal Enthusiasts: Nevada offers considerably more freedom compared to other states, allowing ownership of species like big cats and non-human primates.
- Lower Administrative Barriers: The absence of state permit requirements and associated fees for most species simplifies the acquisition process.
Cons:
- Less Oversight May Lead to Animal Welfare Concerns: The limited state-level regulation raises potential concerns about animal welfare and responsible ownership practices.
- Patchwork of Local Regulations Creates Confusing Landscape: The decentralized regulatory system can be challenging to navigate, requiring diligent research at the county and municipal levels.
- Clark County (Las Vegas) Restrictions: Clark County, home to Las Vegas, maintains significantly stricter regulations than the state, prohibiting many exotic animals otherwise allowed under Nevada law.
Tips for Prospective Owners:
- Research Local Ordinances: Always check county and city ordinances before acquiring an exotic animal. This is the most crucial step to ensuring legal ownership.
- Contact Nevada Department of Wildlife: Consult the Nevada Department of Wildlife for information on protected native species and any restrictions that may apply.
- Clark County Considerations: Be aware that exotic animal ownership in Clark County (Las Vegas) is significantly more restricted than in rural areas.
Nevada’s permissive approach caters to experienced exotic pet owners seeking greater freedom and less bureaucratic overhead. Learn more about Nevada's Permissive Exotic Animal Laws if you are considering adding a primate companion to your family. This system's success is evident in the presence of numerous private collections and even high-profile exotic animal sanctuaries. However, potential owners must understand the responsibilities that come with this freedom, including the need to thoroughly research local regulations and prioritize the welfare of their animals. This decentralized approach is a key element when comparing exotic pet laws by state and demonstrates a unique balance between individual liberty and localized control.
3. California's Strict Exotic Animal Prohibitions
California stands out when discussing exotic pet laws by state due to its particularly stringent regulations. The state maintains one of the nation's most restrictive approaches to exotic pet ownership, effectively prohibiting virtually all exotic mammals, many reptiles, and certain bird species from private ownership through its 'restricted species laws'. This comprehensive ban aims to protect public safety, prevent invasive species introductions, and reduce the demand for exotic wildlife trafficking. These laws make California a challenging environment for exotic pet enthusiasts.

California's approach is characterized by a detailed list of restricted species maintained by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW). While limited permits are available, they are typically granted only for educational, exhibition, or research purposes, making private ownership exceptionally difficult. Enforcement of these regulations is strict, with significant penalties for violations. A grandfather clause exists for certain animals owned before the restrictions were implemented, but acquiring new exotic pets is generally prohibited.
Features of California's Exotic Pet Laws:
- Nearly comprehensive ban on exotic mammal ownership.
- Detailed restricted species list maintained by the CDFW.
- Limited permits available primarily for educational, exhibition, or research purposes.
- Strict enforcement with substantial penalties for violations.
- Grandfather clause for some animals owned before the restrictions.
Pros:
- Strong protections against invasive species introduction: The strict regulations help safeguard California's native ecosystems from the potentially devastating impacts of non-native species.
- Reduced public safety risks from dangerous animal escapes: By limiting the ownership of potentially dangerous animals, the laws minimize the risk of escapes and subsequent harm to the public.
- Decreased demand for exotic wildlife trafficking: The restrictions help curb the illegal trade of exotic animals, protecting vulnerable populations in the wild.
- Fewer abandoned exotic animals requiring rescue: Stricter laws can lead to fewer impulsive purchases and subsequent abandonments of exotic pets, reducing the burden on animal rescue organizations.
Cons:
- Severely limits options for exotic animal enthusiasts: The laws significantly restrict the choices available to individuals interested in keeping exotic pets.
- Complex permit process for qualifying educational facilities: Even for legitimate educational or research purposes, obtaining the necessary permits can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- Strict interpretation of regulations even for less dangerous species: The broad scope of the restrictions can impact ownership of even relatively harmless species.
- Drives some exotic pet ownership underground: The strict laws can unintentionally encourage an illicit market for exotic animals.
Examples of California's Exotic Pet Laws in Action:
- The 2016 alligator confiscation from a private home in Thousand Oaks highlights the state's commitment to enforcing its exotic animal regulations.
- The state's ban on ferrets, while seemingly less impactful, has resulted in an estimated 100,000+ illegal ferrets being kept in California, demonstrating the unintended consequences of such restrictive laws.
Tips for Navigating California's Exotic Pet Laws:
- Always consult the current restricted species list on the CDFW website before acquiring any non-domestic animal.
- If exotic pet ownership is a priority, consider the legal landscape of neighboring states.
- Join California organizations advocating for responsible exotic pet ownership reform to contribute to potential future changes.
California's strict exotic pet laws, popularized by the CDFW and supported by various animal rights organizations, have shaped the landscape of exotic animal ownership in the state. Cases like Shawn Hendricks' legal battle over his serval cat have further defined enforcement practices. This strict approach, while controversial, underscores California's prioritization of environmental protection and public safety. It's crucial for anyone considering exotic pet ownership in California to be thoroughly informed about these regulations and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
4. Texas Dangerous Wild Animal Act
Navigating exotic pet laws by state can be complex, and Texas exemplifies this with its Dangerous Wild Animal Act. This act deserves its place on this list due to its unique approach, balancing state oversight with significant local control. This framework makes understanding the specific regulations in your area crucial before acquiring an exotic animal.
The Texas Dangerous Wild Animal Act primarily focuses on animals deemed "dangerous," including but not limited to big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, etc.), bears, and apes. Instead of a blanket statewide ban or permitting system, the state delegates much of the regulatory power to individual counties and municipalities. While the state sets baseline requirements for registration of these dangerous species, counties have the authority to enact stricter ordinances, including outright prohibitions on ownership.
How it Works:
The act establishes a framework where:
- State Law Defines Dangerous Animals: The state specifies which species are considered dangerous wild animals.
- Counties Implement Regulations: Counties then develop and enforce their own ordinances regarding the ownership, possession, and sale of these animals within their jurisdictions.
- Registration is Key: At a minimum, owners of regulated species must register their animals with the local authorities.
- Liability Insurance is Mandatory: Owners are required to carry liability insurance with a minimum coverage of $100,000 to protect the public in case of an incident.
- Exemptions Exist: Certain facilities, such as AZA-accredited zoos and bona fide research institutions, are exempt from these regulations.
Examples of Implementation:
The varying levels of local control create a patchwork of regulations across the state. For example, Harris County (Houston) maintains stringent regulations, making it challenging to own a dangerous wild animal within its boundaries. Conversely, some rural counties have minimal oversight. The Tiger Creek Animal Sanctuary in Tyler, which houses over 40 big cats, operates successfully under Texas regulations, demonstrating how responsible ownership is possible within this framework.
Pros:
- Balances State and Local Control: This allows for tailored regulations to suit the specific needs and concerns of each community.
- Minimum Safety Standards: The state sets a baseline for safety and public protection.
- Registration System: This helps authorities track the location of dangerous animals within the state.
- Liability Insurance: This financially safeguards the public from potential damages caused by these animals.
Cons:
- Inconsistent Regulations: The county-by-county approach leads to significant variations in rules and enforcement.
- Uneven Enforcement: Some counties may lack the resources and expertise for effective enforcement.
- Limited Scope: The act does not address many exotic species considered less dangerous, potentially creating loopholes.
- Weak State-Level Enforcement: The decentralized nature limits the state's ability to intervene in cases of inadequate local enforcement.
Tips for Prospective Owners:
- Contact Your County Sheriff's Office: This is the best first step to understand the specific regulations in your area.
- Verify Both State and Local Ordinances: Don't rely solely on state law; ensure you comply with all local requirements before acquiring any exotic animal.
- Factor in Liability Insurance Costs: The mandatory insurance can be a significant expense and should be considered as part of your ownership planning.
Popularized By: The Netflix documentary "Tiger King" brought national attention to the world of exotic animal ownership in Texas, highlighting both the passionate owners and the regulatory challenges. Organizations like the Texas Humane Legislation Network continue to advocate for stronger regulations at the state level.
This complex system requires diligent research. While providing flexibility, it places the onus on the potential owner to understand and comply with the varying local regulations. Failing to do so can result in legal penalties and potentially endanger both the animal and the public.
5. Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act
The Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act stands as a landmark piece of legislation in the landscape of exotic pet laws by state. Born from tragedy, the Act drastically altered Ohio's approach to exotic animal ownership, transforming it from one of the nation's least restrictive states to one of the most stringent. This shift followed the infamous 2011 Zanesville incident, where Terry Thompson released 56 dangerous animals, including lions, tigers, and bears, before taking his own life. This shocking event exposed the significant public safety risks associated with lax exotic animal ownership regulations and prompted a swift and dramatic legislative response. This is why the Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act deserves a prominent place on any list of exotic pet laws by state – it serves as both a cautionary tale and a model for stricter regulation.
The Act, implemented in 2012, effectively bans new private ownership of dangerous wild animals, including lions, tigers, bears, alligators, certain monkeys, and large constrictor snakes. This near-complete ban is a core feature of the law, designed to prevent future incidents like the Zanesville tragedy.
Key Features of the Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act:
- Near-Total Ban on New Ownership: Acquisition of regulated animals after 2014 is largely prohibited.
- Grandfather Clause: Owners possessing these animals before 2014 were allowed to keep them, but only under stringent conditions. These include:
- Mandatory Permitting: Owners had to register their animals and obtain a permit, demonstrating compliance with strict regulations.
- Microchipping: All regulated animals must be microchipped for identification purposes.
- Liability Insurance: Significant liability insurance coverage is required to protect against potential damages caused by the animals.
- Housing, Care, and Security Standards: Detailed regulations dictate enclosure specifications, animal care protocols, and security measures to prevent escapes.
- Regular Inspections: Facilities housing these animals are subject to routine inspections to ensure compliance.
Pros:
- Enhanced Public Safety: The Act dramatically reduces the risk of dangerous wild animal escapes and interactions, safeguarding the public.
- Improved Animal Welfare: The strict standards for care ensure a higher level of welfare for the animals under the Act's purview.
- Emergency Responder Awareness: The registration system provides crucial information to emergency responders, enabling them to prepare for encounters with dangerous animals.
- Owner Financial Responsibility: The liability insurance requirement ensures owners are financially responsible for any damages their animals may cause.
Cons:
- Effective End to Private Ownership: The Act effectively ended new private ownership of many exotic species in Ohio.
- High Compliance Costs: Grandfathered owners face substantial costs (often exceeding $1,000 annually) to meet the Act's requirements, forcing some to surrender their animals.
- Strain on Rehoming Resources: The influx of surrendered animals strained the limited resources of sanctuaries and other facilities equipped to care for them.
Examples and Impact:
- The 2011 Zanesville incident serves as the starkest example of the dangers of unregulated exotic animal ownership and directly prompted the Act's implementation.
- By 2020, the Ohio Department of Agriculture reported only 64 permitted dangerous wild animal owners remaining, demonstrating the significant impact of the legislation.
Tips for Prospective Exotic Pet Owners in Ohio:
- Focus on Non-Regulated Species: If you are interested in exotic pet ownership in Ohio, concentrate on species not covered by the Dangerous Wild Animal Act.
- Contact the Ohio Department of Agriculture: Before acquiring any unusual animal, contact the Ohio Department of Agriculture to verify its legality and any applicable regulations.
- Support Accredited Sanctuaries: Consider supporting accredited sanctuaries that provide care for surrendered exotic animals.
Key Figures and Organizations:
- Terry Thompson: The individual responsible for the Zanesville animal release.
- Jack Hanna: Former Columbus Zoo director and a prominent advocate for stronger exotic animal regulations.
- Ohio Association of Animal Owners: This organization challenged certain aspects of the regulations in court.
The Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act represents a significant turning point in exotic animal regulation. While controversial, it serves as a powerful example of how a state can prioritize public safety and animal welfare through comprehensive legislation. For anyone considering exotic pet ownership, understanding the implications of this Act and similar laws in other states is crucial.
6. Arizona's Tiered Exotic Animal Regulation
Arizona stands out when examining exotic pet laws by state due to its nuanced, two-tiered system. This approach acknowledges the diverse needs of both wildlife conservation and responsible exotic pet ownership. Instead of a blanket ban or overly permissive regulations, Arizona utilizes a flexible framework that balances state oversight with significant local control. This deserves its place on the list because it demonstrates a practical, albeit complex, model for exotic animal regulation.
How it Works:
Arizona's system primarily focuses state regulation on native wildlife and a specific list of "restricted live wildlife," employing standard and special licenses for these animals. The standard license permits ownership under specific conditions, while the special license caters to educational or exhibition purposes, such as those held by facilities like Out of Africa Wildlife Park. However, for many non-native exotic pets not defined as restricted wildlife, the state defers regulatory power to individual counties and municipalities. This delegation creates considerable variation in local ordinances, resulting in a complex regulatory landscape.
Features and Benefits:
- State Focus on Native Wildlife: Concentrates resources on protecting indigenous species and preventing the release of non-native wildlife that could disrupt the ecosystem.
- Two-Tier Permit System: Offers clear pathways for private ownership (standard license) and educational/exhibition purposes (special license).
- Strong Local Control: Empowers counties and municipalities to tailor regulations to their specific needs and concerns, allowing for flexibility.
- Allowance of Many Non-Native Species: While some species are restricted statewide, Arizona's framework allows for the private ownership of many exotic animals with the proper permits, catering to experienced exotic pet owners seeking unique companions.
- Detailed Record-Keeping: Mandates thorough documentation for permitted animals, promoting responsible ownership and facilitating tracking.
Pros:
- Flexible Framework: Adapts to diverse regional concerns across the state.
- Opportunity for Private Ownership: Provides avenues for legally owning a variety of exotic pets, offering options for affluent enthusiasts and experienced keepers.
- Special Licenses for Education/Exhibition: Supports organizations like The Phoenix Herpetological Sanctuary in their conservation and educational efforts.
- Focus on Preventing Invasive Species: Prioritizes ecosystem health by controlling the introduction of non-native wildlife.
Cons:
- Complexity and Variation: Navigating the varying county and municipal regulations can be challenging for potential owners.
- Stricter Local Ordinances: Counties like Maricopa (which encompasses Phoenix) often have stricter regulations than the state level, posing challenges for residents in these areas.
- Limited State Enforcement Resources: Decentralized enforcement can lead to inconsistencies and difficulties in ensuring compliance.
- Overlapping Authority: The interplay between state and local regulations can create confusion for exotic pet owners.
Examples:
- Out of Africa Wildlife Park: Operates under Arizona's special license provisions, showcasing a successful implementation of the tiered system for exhibition purposes.
- The Phoenix Herpetological Sanctuary: Collaborates with Arizona Game and Fish, often housing confiscated reptiles, highlighting the practical application of the regulations and the importance of resources for specialized care.
Tips for Prospective Owners:
- Consult with Authorities: Before acquiring any exotic animal, contact both the Arizona Game and Fish Department and your local animal control office. This is crucial for navigating the layered regulations and understanding specific requirements.
- Join the Arizona Exotic Animal Association: This organization offers valuable resources and guidance on navigating the state's exotic animal regulations.
- Verify Insurance Requirements: Insurance needs vary significantly based on species and location. Ensure you have adequate coverage to protect yourself and your animals.
Why This Approach Matters:
Arizona's system provides a valuable case study in balancing conservation with the desires of exotic pet owners. While the complexities present challenges, the tiered approach allows for a degree of flexibility and local autonomy that many other states lack. This model is particularly relevant for experienced exotic pet owners, first-time adopters, and even veterinarians specializing in exotic species, as it provides a framework—albeit a complex one—for responsible exotic animal ownership. By understanding this system, individuals can navigate the regulations effectively and contribute to responsible exotic pet keeping within Arizona.
(No website link was provided for general Arizona exotic animal regulations.)
7. New York's Comprehensive Exotic Animal Ban
New York State takes a firm stance against exotic pet ownership, implementing one of the nation's most restrictive sets of exotic pet laws by state. The state's Dangerous Animal Act and subsequent regulations establish a near-blanket prohibition on owning "wild animals," significantly limiting the options for exotic pet enthusiasts. This approach aims to prioritize public safety and prevent issues associated with exotic animal abandonment and illegal wildlife trafficking. This entry explains why New York's approach deserves a prominent place on any list concerning exotic pet laws by state.
How It Works:
New York's ban broadly defines "wild animals," encompassing a wide range of species including big cats (lions, tigers, leopards, etc.), bears, primates, certain reptiles, and many others. While limited exemptions exist for research and exhibition purposes with appropriate permits, private ownership is largely prohibited. Furthermore, the state grants municipalities the authority to enact even stricter regulations. This has led to New York City implementing additional restrictions on numerous species that are conditionally allowed in other parts of the state, creating a two-tiered system within New York's exotic pet laws by state.
Examples of Implementation:
The strict enforcement of these exotic pet laws by state is evident in several high-profile cases. The discovery of "Ming," a full-grown tiger living in an apartment in Harlem in 2003, highlighted the challenges posed by illegal exotic pet ownership and spurred further regulatory action. The extensive nature of the ban has also led to the creation of several out-of-state animal sanctuaries specifically designed to accommodate animals confiscated in New York.
Pros:
- Strong Public Safety Protections: Restricting ownership of potentially dangerous animals minimizes the risk of attacks and injuries to the public.
- Reduced Abandonment: The ban helps prevent the abandonment of exotic pets that owners can no longer care for, a common problem in states with less stringent exotic pet laws by state.
- Clear Regulatory Framework: The comprehensive nature of the ban leaves little room for ambiguity, providing a clear understanding of what is and isn't allowed.
- Combats Illegal Wildlife Trafficking: The strict regulations serve as a deterrent against the illegal wildlife trade.
Cons:
- Limited Ownership Options: The ban severely restricts the options for individuals interested in owning exotic pets in New York.
- Limited Grandfathering: Existing owners may face challenges due to limited grandfather provisions within these exotic pet laws by state.
- Overly Broad Definitions: The broad definition of "wild animals" can sometimes capture species that pose minimal risk.
- Two-Tiered System: The stricter regulations in NYC create inconsistencies in exotic pet ownership legality across the state.
Tips for Prospective Owners:
- Consult the New York Department of Environmental Conservation (NYDEC) before acquiring any unusual pet to ensure compliance with the state's exotic pet laws by state.
- Be acutely aware of the differences between upstate and NYC regulations. Many animals permissible upstate are strictly prohibited within city limits.
- Research species specifically exempted from the ban, such as certain reptiles, if you're determined to own an exotic pet in New York.
Popularized By:
The NYDEC's enforcement actions and high-profile confiscations, such as the "Ming" the tiger case, have brought significant attention to New York's stringent approach to exotic pet ownership. These events have solidified the state's position as a leader in restricting exotic pets and contribute to its importance in discussions surrounding exotic pet laws by state.
While New York's approach may be frustrating for some exotic pet enthusiasts, its focus on public safety and animal welfare makes it a crucial example when comparing exotic pet laws by state. The comprehensive nature of the ban underscores the importance of responsible pet ownership and the need for regulations to protect both people and animals.
Exotic Pet Law Comparison by State
| 🏛️ Law Title | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Florida Exotic Pet Regulations | Moderate to High: Three-tier system with strict permits and inspections | High: Permit fees, insurance, record-keeping, annual inspections | Ensures animal welfare and public safety | Owners seeking regulated exotic pet ownership | Clear framework, supports many species, annual inspections |
| Nevada's Permissive Exotic Animal Laws | Low: Minimal state permits, relies on local rules | Low: No state permit fees or insurance generally | Potential animal welfare risks due to less oversight | Enthusiasts wanting fewer restrictions | High ownership freedom, low administrative barriers |
| California's Strict Exotic Animal Prohibitions | High: Nearly comprehensive bans, detailed restricted species list | Moderate: Permit process for exempted entities | Strong public safety and invasive species prevention | Public safety and wildlife protection | Strong protections, reduces trafficking and escapes |
| Texas Dangerous Wild Animal Act | Moderate: Delegated local control with baseline state regs | High: Registration, insurance ($100,000 minimum) | Balances local flexibility with minimum safety standards | Owners in counties with regulations | Local control with state baseline, liability coverage |
| Ohio Dangerous Wild Animal Act | High: Comprehensive bans, strict permits, regular inspections | High: Insurance, compliance costs, microchipping | Strong safety and welfare, limits new ownership | High safety priority, emergency responder awareness | Strong protections, clear emergency info, reduces ownership |
| Arizona's Tiered Exotic Animal Regulation | Moderate to High: Two-tier permits plus varied local rules | Moderate: Permit fees and record-keeping vary | Flexible regional regulation, prevents wildlife release | Owners needing permits with local support | Flexible, accommodates regional needs, special licenses |
| New York's Comprehensive Exotic Animal Ban | High: Blanket bans with limited exemptions, strict enforcement | Moderate: Enforcement and permits for exemptions | Maximizes public safety, deters illegal trafficking | Strict regulation advocates | Clear framework, strong deterrent, reduces abandonment |
Ready to Welcome an Exotic Companion?
Navigating the world of exotic pet ownership requires careful consideration of the varying regulations across different states. As we've explored, from Florida's specific permits to California's strict prohibitions, and the nuanced approaches in states like Nevada, Texas, Ohio, Arizona, and New York, understanding the specific exotic pet laws by state is paramount. These laws are designed to protect both the animals and the public, ensuring responsible ownership and ethical practices. Mastering these regulations is not just about compliance; it's about creating a safe and enriching environment for your unique companion. For veterans who also happen to be exotic pet owners, understanding state-specific benefits can be helpful when relocating with your unique companions. Resources like the 2025's Guide: Veterans Benefits by State from Homefront Group can be invaluable during these transitions.
Ultimately, responsible exotic pet ownership involves diligent research, preparation, and a commitment to providing the best possible care. The rewards, however, are immense. Sharing your life with an extraordinary animal companion can be a deeply enriching experience.
Ready to embark on this exciting journey? Primate Pets can provide expert guidance on navigating exotic pet laws by state, ensuring you're fully prepared to welcome your new companion into a loving and compliant home. Let us help you build the perfect habitat and provide the specialized care your unique pet deserves.
Article created using Outrank




